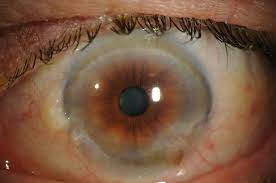
CORNEAL EPITHELIAL DEFECTS

Corneal Epithelial is the outermost layer of the cornea in the eye. A healthy corneal epithelium is vital in protecting the eye against infection and structural damage to deeper tissues. A Corneal Epithelial Defect occurs when there exists a reoccurring condition that causes the failure of the mechanisms promoting corneal epithelialization. The common symptoms could include the following:
- Pain in eye even when blinking or general eye movement
- Tearing in eyes
- Feeling a foreign body sensation in the affected eye
- Blurry vision
- Redness in eye

Causes of Corneal Epithelial Defects
These Corneal epithelial defect could occur due to various causes including the following:
- Trauma to eyes such as entry of foreign object in eye or chemical exposure or burns etc
- Inflammatory disease combined with other conditions.
- Neurotrophic disease causing corneal sensation such as diabetes
- Decreased tear production
- Limbal stem cell deficiency
- Infections including ulcers
Can Corneal Epithelial Defects be prevented?
The prevention of the condition in many cases is possible. Taking simple regular precautions to taking extra care when exposed to certain conditions which causes risk can do a lot for protecting the eyes. Wearing protective eyewear, safety glasses during risky activities like mechanical repair work, painting etc can prevent foreign bodies from entering the cornea. Also maintaining a good eye hygiene practices such as not touching the eyes with unwashed fingers, not sleeping in contact lenses, etc can prevent infections. Treatment for underlying diseases or condition that is causing the defect such as dry eyes, treatment of can protect the corneal epithelium.


- Typically lubrication with artificial tears or lubricating ointment could be provided for comfort and prevent infection. Other methods to increase retention of natural teras to facilitate healing are also used.
- Antibiotics use for small defects is recommended along with observation to prevent possible infection
- Tarsorrhaphy is a procedure that involves partial or complete closure of the eyelid fissure. This allows the ocular surface to heal itself.
- Bandage contact lens or BCL are used to protect the corneal surface from mechanical trauma from the eyelids.
- Specific medication such as Tetracyclines may aid in corneal wound healing
- Use of topical may also be recommended in certain conditions
Before any treatment, thorough history is required to determine the etiology of the corneal defect. A thorough exam of both eyes is needed as in many cases both eyes can be affected. Patients should follow up regularly to monitor for signs of infection even after treatment.